VASTOGG© Model Nations.
Explore Nations Where VASTOGG© Transformed Their Fortunes.
Singapore

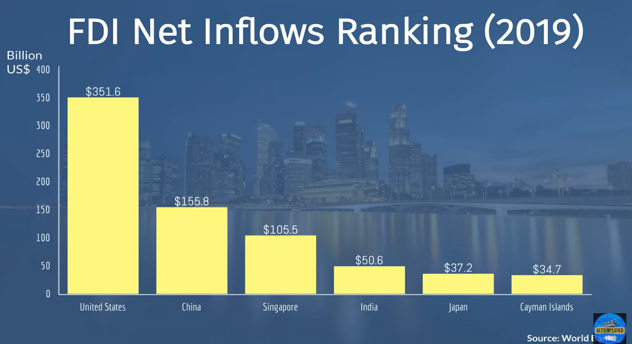
Through strategic implementation of a VASTOGG© like model, Singapore transformed from a poor 3rd world country in the 1960’s to the one of the nations with the highest Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) and to a first world country.
Brief History
Singapore boasts of a long and rich history from the 14th Century. The Island nation originally was inhabited by fishermen and pirates, and it served as an outpost for the Sumatran empire of Srīvijaya.
In December 1941 the Japanese landed in northern Malaya and southern Thailand on the Malay Peninsula. They quickly gained air and naval superiority in the region, and by the end of January 1942 they had overrun the peninsula and were opposite Singapore Island. The Japanese crossed the Johor Strait on February 8, 1942, and the British command surrendered the island and city one week later. Singapore remained in Japanese hands until September 1945.
Singapore joined the Federation of Malaysia on its formation in September 1963 with the Ruling People’s Action Party (PAP), led by Lee Kuan Yew.
Economy
The economy of Singapore is a highly developed mixed market economy with dirigiste characteristics Singapore's economy has been consistently ranked as the most open in the world, the joint 4th-least corrupt, and the most pro-business.
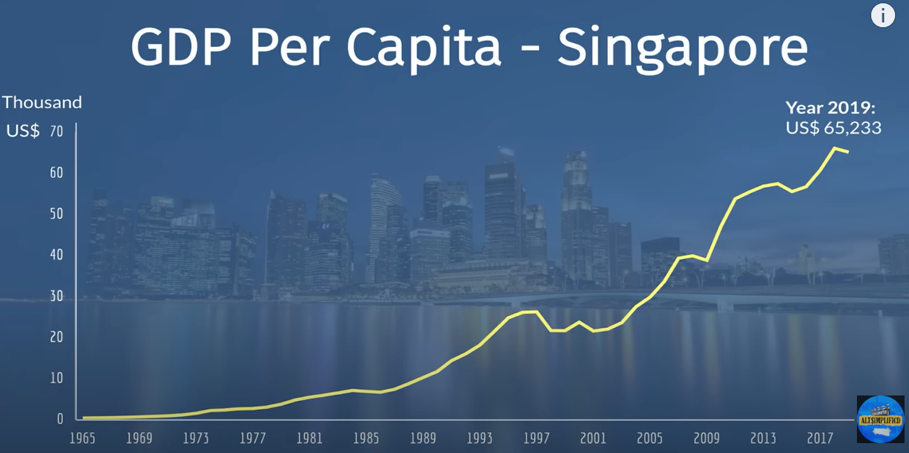
In the 1960s, the city-state of Singapore was an undeveloped country with a GDP per capita of less than U.S. $320. Today, it is one of the world's fastest-growing economies. Its GDP per capita has risen to an incredible U.S. $60,000, making it one of the strongest economies in the world.
Population
Singapore's population growth from 1963 has been on average 2.92% from 1,762,516 people in 10=963 to 6.04 million people in 2024.
Value System
Singapore has five shared values;
1) Nation before community and society above self.
2) Family as the basic unit of society.
3) Community support and respect for the individual.
4) Consensus, not conflict.
5) Racial and religious harmony.
The government engaged Christians, Muslim, Tamil and Chinese groups as well as actively promotes family values as essential for laying a solid foundation for the country's long-term development.
Greatest Achievement
As part of Singapore’s greatest achievement, was to design a country that was based on values, meritocracy, strategic positioning and high-level commitment against corruption and wastage.
Japan

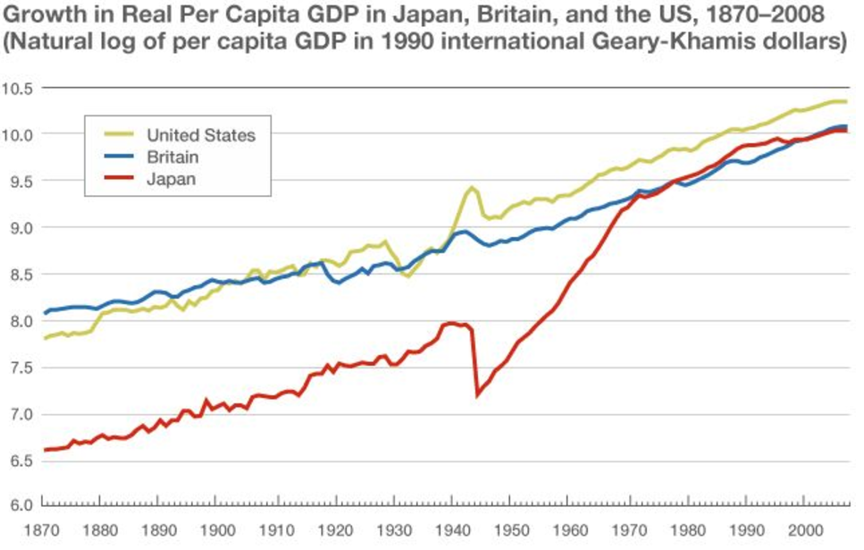
Japan today stands as a highly industrialized country. Japan’s economy was in 2023 ranked fourth in the world, behind the United States, China, and Germany. Japan is a first world country that was able to turnaround its fortunes despite facing one of the worst catastrophes in modern history. A deep evaluation of the Japan’s economic and social miracle points towards a perfected implementation of the VASTOGG © Philosophy in governance.
Brief History
Japan is nation with very rich history and culture. The first human inhabitants of the Japanese archipelago have been traced to the Paleolithic, around 38–39,000 years ago. Over the centuries, Japan has undergone various transitions with the modern-day Japan history beginning in 1868 with the Meiji era, when the country transformed from an isolated feudal island into an empire. The Meiji era saw Japan rapidly industrialize and modernize and become a great power. Between 1912 and 1926 (The Taishō period) Japan saw the development of democracy and civilian culture, but the military remained powerful and overruled civilian leaders. Between 1931–1941, Japan invaded Manchuria and became involved in a war with China. Japan then attacked the United States and European colonial powers in 1941, entering World War II as an Axis power. In 1945, Japan surrendered after the atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki, and the Soviet invasion of Manchuria. The Allies occupied Japan until 1952. In 1947 Japan enacted a new constitution that established it as a parliamentary democracy and constitutional monarchy.
Impact of Atomic Bombing
In the second world war, the United States dropped atomic bombs on Hiroshima and Nagasaki, respectively. These bombings were the first use of nuclear weapons in war. The bombings killed an estimated 140,000 people in Hiroshima and 74,000 in Nagasaki. Many survivors later developed leukemia, cancer, or other radiation-related illnesses.
More than 2 million people died in Japan during the war, including more than 500,000 civilians. The atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki killed more than 200,000 people. Major cities like Tokyo were destroyed by conventional bombing. The surrender led to a collapse of value standards for many people, and social instability among those who lost their patriotic identity. The surrender led to a collapse of value standards for many people, and social instability among those who lost their patriotic identity.
The atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki had a devastating impact on Japan's economy, causing widespread damage to infrastructure, industrial plants, and critical areas: The industrial production index dropped from 149 in 1940 to 31 in 1946. Metallurgical, chemical, engineering, and textile firms lost between 10–20% of their production. Critical infrastructure like bridges, roads, and railways were badly damaged. Entire neighborhoods were destroyed, and 70,147 buildings in Hiroshima were destroyed or partially destroyed. The war wiped out many of the gains which Japan had made since 1868. About 40% of the nation's industrial plants and infrastructure were destroyed, and production reverted to levels of about fifteen years earlier.
Japan Value System
In Japan, some of the core values are thinking of others, doing your best, not giving up, respecting your elders, knowing your role, and working in a group. These concepts are taught explicitly and implicitly from nursery school into the working world.
Japan Economy Today
Japan's economy experienced a period of rapid growth after World War II, known as the Japanese economic miracle. From 1946 to 1973, Japan's real GNP grew at an annual rate of 9.6%.


United Arab Emirates

Through strategic implementation of a VASTOGG© like model, Singapore transformed from a poor 3rd world country in the 1960’s to the one of the nations with the highest Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) and to a first world country.
Brief History
The United Arab Emirates (UAE) has a rich history that includes trade, Islam, and colonial rule: The strategic UAE's location between Europe and the Far East made it a valuable destination for merchants from India and China, and for Europeans like the Portuguese, Dutch, and British. UAE is an Islam nation that dates to 630 C.E. Before the UAE's independence, the seven emirates were part of the Trucial States, a British protectorate.
The UAE was formed in December 1971, except for Ras Al Khaimah, which joined in 1972.
Population
From 1960 to 2023 the population of the United Arab Emirates increased from 92,417.00 to 9.52 million people.
Value System
The United Arab Emirates (UAE) has a value system based on openness, tolerance, the rule of law, and the preservation of rights. The UAE's culture also emphasizes hospitality, generosity, respect, and family cohesion
Economy
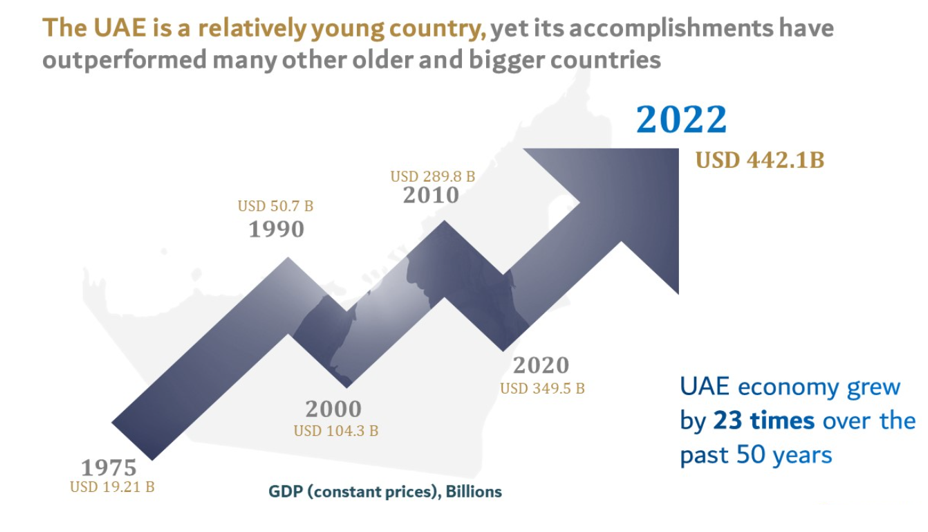
The discovery of oil in Abu Dhabi in the early 1960s led to calls for unification among the emirates. The UAE GDP has grown from $19.21B in 1960’s to $442B in 2022. The United Arab Emirates (UAE) has been the top U.S. export market in the Middle East and Africa region since 2009 and is a global hub for over 1,500 American companies doing business throughout the Middle East, Africa, Europe, and Asia.